心衰你會處理了嗎?
最近三天收治了三個不同類型的心衰。
先說第一個,先天心的心力衰竭。
患者,男,35歲。
主訴:反覆氣促,咳嗽,咳痰5年餘,加重伴咳粉紅色泡沫痰1天。
現 病史:患者約五年餘前開始出現活動後氣促,伴有咳嗽、咳痰,痰多為白色粘液痰,多次按「肺炎」治療,可好轉;但氣促呈進行性加重,逐漸出現端坐呼吸到夜間 陣發性呼吸困難,伴有全身發紫。一天前再次出現咳嗽、咳痰,氣喘明顯,伴有高熱,右側胸痛,呈牽拉痛,在社區門診治療無好轉,並出現咳粉紅色泡沫痰而轉診 至我院。自本次加重以來,尿量明顯減少,胃納,精神,睡眠差。
既往史:兒時發現先天性心臟病:房間隔缺損,未作任何處理。
查體:T:39.3。C Bp:140/70mmHg P:115bpm R:28bpm SaO2%: 43%
神 清,慢病急性重病容,口唇,肢端發紺明顯,四肢冰冷,但無汗。無明顯貧血貌,無黃染。端正位下頸靜脈充盈明顯,胸廓呈雞胸畸形,雙下肺可聞及細囉音,雙肺 均可聞及少量的哮鳴音。心前區見抬舉樣搏動,心界明顯坐下擴大,心率115bpm,律齊,胸骨左緣第2、3肋間可聞及2~3級的雙期雜音,未及震顫。腹未 見明顯陽性體徵。雙下肢無浮腫。
輔查:
胸片:先天心,考慮房缺;右下肺炎。
心電圖:明顯左右房增大。
血常規:wbc:23.6x109/L, N%:0.881, HGB:115g/L PLT 103x109/L
電解質,腎功能均正常。
請教大家以下幾個問題:
1、首先是診斷。
2、這個病人你考慮存在肺水腫嗎?畢竟胸片沒報,只是有侷限的右下肺感染?是什麼導致粉紅色泡沫痰?
3、這個病人的心衰是肯定存在的,而且已經存在了右向左分流,假如表現為典型的急性左心衰,你會怎樣處理?利尿,擴管效果不佳,這個病人能夠使用正性肌力藥物嗎?比如洋地黃,磷酸二酯酶抑制劑,多巴酚丁胺等,怎樣使用,要注意什麼,要配合哪些藥同時使用?
第二個是慢支 COPD 肺心病,典型急性左心衰伴有頑固性低氧血症而來,這時候你會怎處理?
第三個是風心患者 急性左心衰而來,查體可見嚴重的二尖瓣面容,心尖區可聞及舒張期隆隆樣雜音,是否存在嚴重的二尖瓣狹窄,暫時無法明確,常規利尿,擴管效果不佳,此時怎麼辦?
由此聯想到,高血壓導致的急性心衰,心梗導致的心衰(又分前壁、下壁、右室),心肌炎等,我們應怎樣處理?這麼多種心衰他們之間有什麼不同,又有什麼共同的本質,需要注意哪些因素或者有哪些技巧,你能說出來嗎?你會處理了嗎?
以上都是指慢性心衰的基礎上發作的急性心衰,這個和單純的急性左心衰有什麼區別?期待著你們給我答案。
看到有人點到我的名字,咦, 有點忘了有貼過這樣的帖子,連過去一看,哇 !有一年多了哩! 把它縫接過來,當作溫故知新。
2008年一月Critical care medicine 有一篇以臨床實務觀點出發的指南,以簡明的臨床情境分類指引到院前以及到院早期的處理原則,可供吾人一定的參考,尤其呼應樓主『搶救』急性心衰的主旨。
Practical recommendations for prehospital and early in-hospital management of patients presenting with acute heart failure syndromes.
Crit Care Med. 2008 Jan;36(1 Suppl):S129-39. Review
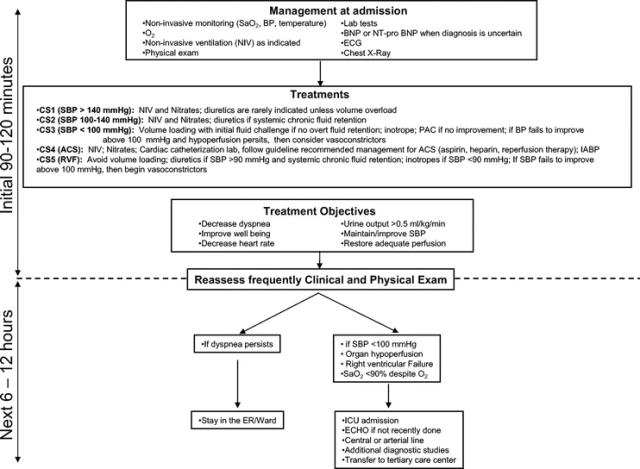
臨床情境:
處理流程:
前帖 Digoxin 風華再現,裡面提到的推荐閱讀:State of art: Acute Heart Failure Syndome. Review. 裡面有幾張表格,可以互補前面兩張的不足。
AHFS 診治的四個階段:
- initial or early phase (i.e., emergency department) 急性期
- in-hospital phase住院期
- pre-discharge phase 出院期 (3,,4可以合起來看)
- early post-discharge phase
| 1. Treat immediate life-threatening conditions/stabilize patient | Life-saving measures may precede or parallel diagnostic evaluation (i.e., unstable arrhythmia, flash pulmonary edema, STEMI) |
| 2. Establish the diagnosis | Based on medical history, signs (JVD, S3, edema), symptoms (dyspnea), biomarkers (e.g., BNP) and CXR |
| 3. Determine clinical profile and begin initial treatment | Key components include HR, BP, JVP, presence of pulmonary congestion, ECG, CXR, renal function, troponin, BNP, pulse oximetry, history of CAD |
| 4. Determine and manage the cause or precipitant | Such as ischemia, hypertension, arrhythmias, acute valvular pathologies, worsening renal function, uncontrolled diabetes, and/or infectious etiologies is critical to ensure maximal benefits from HF management |
| 5. Alleviate symptoms (e.g., dyspnea) | Usually a diuretic with or without other vasoactive agents. Morphine may also be used for pulmonary edema† |
| 6. Protect/preserve myocardium and renal function | Avoid hypotension or increase in HR, particularly in patients with CAD. Use of inotropes should be restricted to those with low-output state (low BP with organ hypoperfusion) |
| 7. Make disposition | Majority are admitted to telemetry, with a small number discharged home. Robust evidence to support risk stratification and disposition identifying the low-risk patient for safe discharge with close outpatient follow-up is lacking |
住院期:
最重要的治療思路是要釐清臨床情境,也就是個體化治療方案,這張可以跟第一張合併參看 。